Ancient India Facts
The time span of ancient India stretches from 5000 BC to roughly about 10th century AD. This is a very long time line and there are many startling facts about ancient India. Since all the facts cannot be made available, a few important ones are mentioned here to enumerate the achievement of ancient India.
Ancient India in Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus valley civilization was one of the most advanced civilizations of the world. This is testified by its sense of town planning and other details of the urban landscape. The script of Indus civilization was pictorial in and there were more than 600 picture-letters and 60 original letters. The remains of a dockyard in Lothal in Gujarat of Indus period testify the trade relations of Indus people with western Asia. In Harappan culture the weight (for measuring) were 16 or of its multiplied numbers.
Ancient India in Vedic age
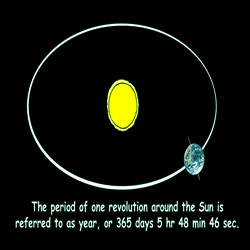
Earth to orbit the sun During the Vedic age the river that was worshipped by Aryans was Sindhu. India drives its name from River Indus that’s ‘Sindhu’ where the first Aryan settlers established their home. Sanskrit is the most ancient language of the world that was developed during the Vedic age. Women held prominent position during Vedic age. The prominent female sages during that period were Lopamudra, Ghosa, Shachi and Poulomi.
The earliest school of medicine known as Ayurveda originated during the Vedic age. Ayurveda was developed by Charaka, considered to be the father of medicine who consolidated it in his book charakasmitha.
During the Vedic age prominent Ayurveda acharyas were Acharya Ashwini Kumar, Dhanvantari, Banabhatt, Sushrut, Madhav, Jeevan and Lolimbaraja. The great physician of ancient India who conducted complicated surgeries was Sushruta. Sushruta is called the father of surgery and he compiled his findings in the book Sushrutasamitha.
The art of Yoga, a form of physical exercise to control diseases was developed by Patanjali a revered sage in ancient India. Taxila and Nalanda were important centres of learning in ancient India. Takshila, establish in 700 BC holds distinction of being world's first university.
The University of Nalanda built in the 4th century BC. It was one of the greatest centres of learning in ancient India. Panini, the Sanskrit grammarian, who lived between 750 and 500 BC, was the first to compose formal grammar through his work Astadhyai.
Two major religions, Buddhism and Jainism were established in India in 500 and 600 BC, respectively. River Ganga was another important river in ancient India. Many settlements, cities and towns developed on the banks of this holy river. Varanasi, also known as Benares, situated on the banks of river Ganga is the oldest, continuously inhabited city in the world The four pieces of Hindu literature; Mahabhanata, Panchatantra, Ramayana, Bhagavad Giva were compiled after the Vedic period.
The records of King Rudradaman I of 150 BC show that Sudarshan Lake at Junagarh was built by Chandra Gupta Maurya. Chandra Gupta Maurya is called Sandrocottus in the Greek writings.
The Grand Anicut, also known as the Kallanai dam was built on the Kaveri River by the Chola king Karikalan in 2nd Century BC. It is considered one of the oldest water-diversion or water-regulator structures in the world.
Trade between India and China was carried on before Gupta age, in 2nd century AD. During the Gupta age, ships and boats were manufactured in large numbers. Gujarat, bengal and Tamil Nadu were the main centres of cotton industry. Some other achievements during the Gupta period were in the field of literature, astronomy, medicine, paintings, sculptures, roads, universities, maths and metallurgy.
Fact about Mathematics in Ancient India

value of 'pi' India invented the Number System. Zero was first used by Aryabhatta. Around 100 BC, the place value system, the decimal system was developed in India.
Budhayana was the first Indian mathematician to calculate the value of 'pi' in the 6th century AD. He explained the concept of Pythagorean Theorem. Quadratic equations were propounded by Sridharacharya in the 11th century AD. Algebra, trigonometry and calculus all came from India.
Fact about Astronomy in Ancient India
Gargi Samhita is a book on astronomy. Aryabhatta, was a great mathematician, astronomer and scientist. Bhaskaracharya, was another the great astronomer and mathematician. He was the first person to calculate the time taken by the earth to orbit the sun. He guessed his calculation to 365.258756484 days in the 5th century AD. Kaundinya, a Brahmin astrologer, was contemporary of Buddha.
Fact about Books in Ancient India
Arthasastra by Kautilya is a book about economic and legal issues during Maurya period. Vishakhadatta's Mudrarakshasa gives a glimpse of Maurya society and culture. Kalidasa in Malvikagnimitram mentions events of the Pushyamitra Sunga's reign. Banabhatta's Harshacharita, deals with the character and achievements of Harshvardhana. Bakpatiraja's Gaudabaho describes how King Yasovarman (725–752) of Kannauj killed the king of Magadha and conquered Gauda.

ShataranjaPoet Bilhana in his Vikramanka Charita described the history of the reign of Chalukya king Vikramaditya VI. Sandhyaakar Nandi's Ramacharita is a description of the reign of Rampal, a king of the Pala dynasty of Bengal.
Kalhana's Rajatarangini is a valuable book on the history of the kings of Kashmir.
Padmagupta's Nabasahasanka Charita, Hem Chandra's Dwasraya Kavya , Nyaya Chandra's Hammir Kavya , Ballal's Bhoja Prabandha contains important historical materials of ancient India.
Reference Books
1. “Indian Scientific Heritage” by Dr.N.GopalaKrishnan
2. “Theorems discovered by Indians” by Dr.N.GopalaKrishnan
3. “India's contribution to World culture” by Sudheer Birodkar
Contribute More Facts